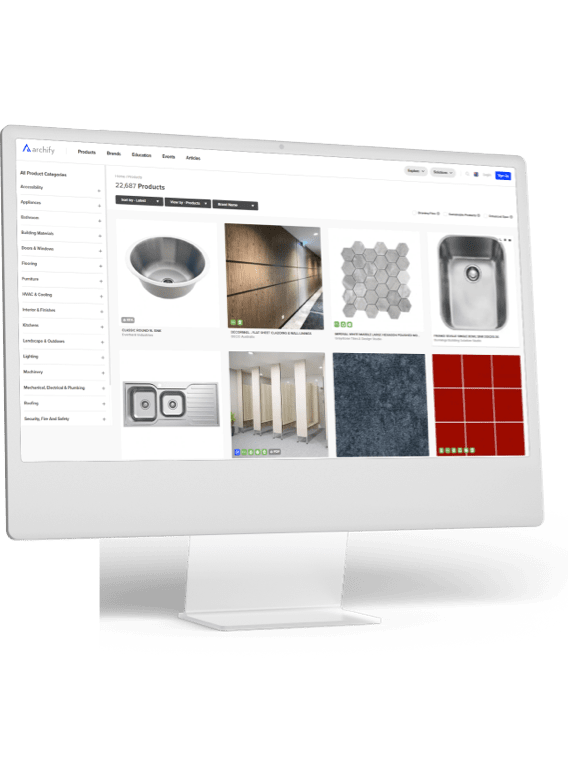
What is Seismic Glass?
Laminated glass performs very well in seismic applications because the plastic interlayer holds most of the glass fragments following cracking, which significantly reduces the potential of glass falling to the ground. In addition, the complete glass unit tends to be retained in the frame.
Where should I use it?
Earthquake-resistant glass should be used in all fenestration in seismic-prone areas. Applications include storefronts, curtain walls and other commercial glazing.
Two major factors need to be examined in any consideration of earthquake-induced glass damage:
• How the glass system performs and responds to racking-type earthquake-induced building deflections such as interstory drift;
• How the glass performs after it has been cracked by frame movements.
The frame is, therefore, an integral part of an earthquake-resistant glazing system. Frames prone to racking during earthquake-induced building movements can cause glass components to crack, and, for some types of glass, to fall in fragments.
What is Seismic Glass?
Laminated glass performs very well in seismic applications because the plastic interlayer holds most of the glass fragments following cracking, which significantly reduces the potential of glass falling to the ground. In addition, the complete glass unit tends to be retained in the frame.
Where should I use it?
Earthquake-resistant glass should be used in all fenestration in seismic-prone areas. Applications include storefronts, curtain walls and other commercial glazing.
Two major factors need to be examined in any consideration of earthquake-induced glass damage:
• How the glass system performs and responds to racking-type earthquake-induced building deflections such as interstory drift;
• How the glass performs after it has been cracked by frame movements.
The frame is, therefore, an integral part of an earthquake-resistant glazing system. Frames prone to racking during earthquake-induced building movements can cause glass components to crack, and, for some types of glass, to fall in fragments.
What is Seismic Glass?
Laminated glass performs very well in seismic applications because the plastic interlayer holds most of the glass fragments following cracking, which significantly reduces the potential of glass falling to the ground. In addition, the complete glass unit tends to be retained in the frame.
Where should I use it?
Earthquake-resistant glass should be used in all fenestration in seismic-prone areas. Applications include storefronts, curtain walls and other commercial glazing.
Two major factors need to be examined in any consideration of earthquake-induced glass damage:
• How the glass system performs and responds to racking-type earthquake-induced building deflections such as interstory drift;
• How the glass performs after it has been cracked by frame movements.
The frame is, therefore, an integral part of an earthquake-resistant glazing system. Frames prone to racking during earthquake-induced building movements can cause glass components to crack, and, for some types of glass, to fall in fragments.
United States